Psycho-motor Therapy

Psycho-motor Therapy
May 6, 2019
- Psychomotor therapy aims to support and aid an individual’s personal development. It is based on a global view of human beings that considers each individual as a unity of physical, emotional and cognitive actualities, which interact with each other and the surrounding social environment.
- Psychomotor specialists study the body and its expressivity. The body is regarded not merely as a mechanism with neurophysiological developments, but also as a thing with deep-rooted emotional traits, which have come about through motor, sensory and emotional experiences, particularly in early-childhood.
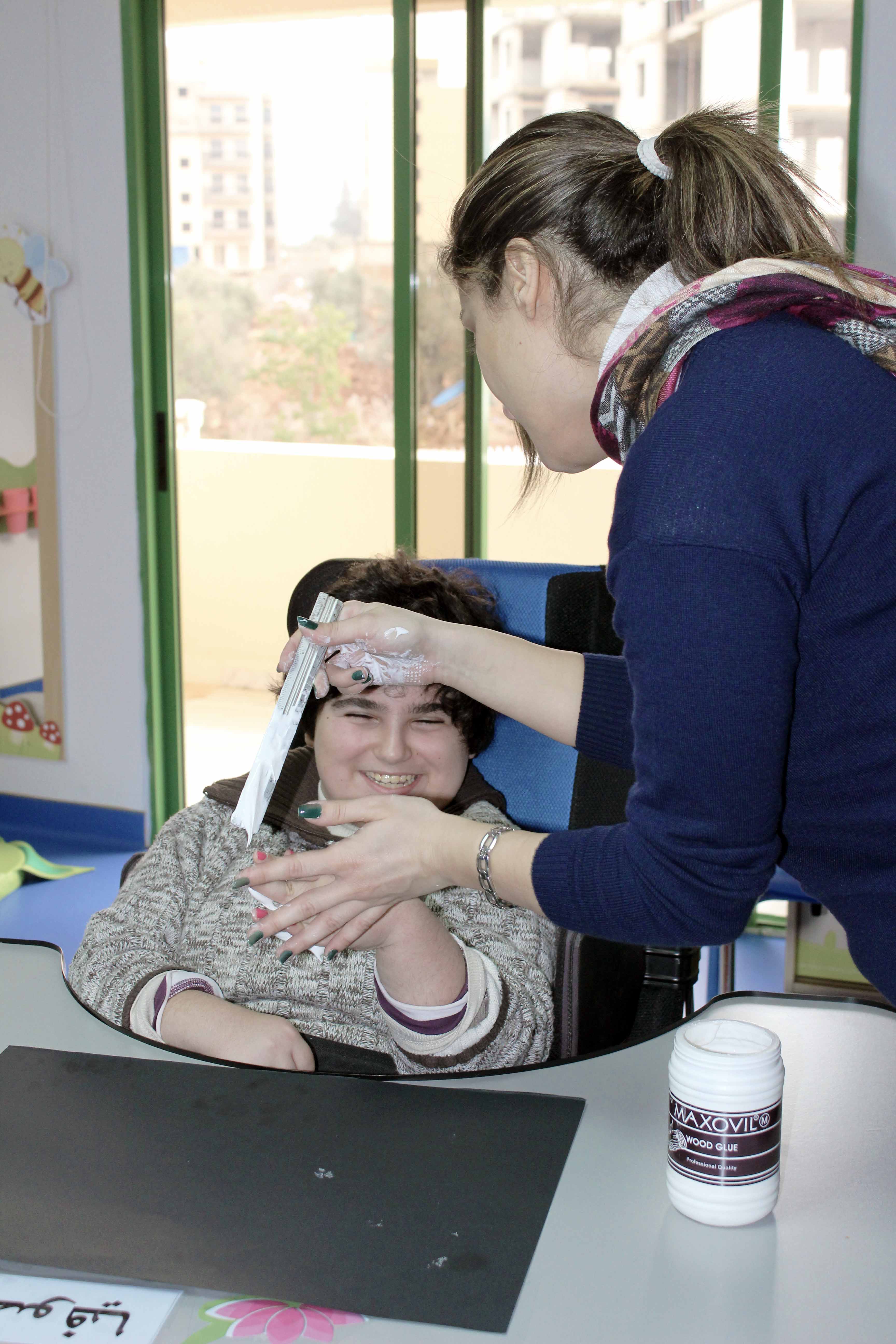
A child will benefit from psycho-motor therapy intervention if they present with any of the following:
- Early Psycho-motor development delay (for infants)
- Motor difficulties (gross/fine motor skills)
- Unusually high or low activity level, (always active or difficulties with attending)
- Unusual fear of movement/heights
- Excessive craving of rough play and/or lack of safety awareness
- Unusual play habits and skills or messy play
- Unusual avoidance of touch or eye contact
- Lack of hand preference
- Poor handwriting/slow written output
- Difficulty with self-care activities including: brushing teeth, combing hair, buttoning a shirt, tying shoes, using utensils such as a spoon or fork.
- Delays in speech (children who have delays in speech often demonstrate Psychomotor difficulties affecting their motor coordination and their cognitive skills)
- Difficulties with cognitive tasks such as following instructions, problem solving and visual organization.
- Delay with drawing skills, copying shapes or letters
- Lack of knowledge in space and time concepts
- Short attention span

PMT focuses on:
- Gross and fine motor skills
- Lateral dominance
- Sensory processing
- Cognitive abilities: visual attention, visual memory, planning and problem solving, visual analysis
- Space and time concepts
- Hand writing skills
- Emotional history affecting activity level, behavior, interaction and cognitive skills (visual attention, memory, planning and problem solving, visual analysis)
- Muscle tone regulation
